|
Thyme is a fragrant, herbaceous plant native to the Mediterranean region, belonging to the mint family. It has been used for thousands of years in cooking, medicine, and even religious rituals. Raw thyme, with its strong, earthy aroma and savory flavor, is widely used in culinary dishes and for its numerous health benefits. It is particularly valued for its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties.
Botanical Characteristics:
Thyme is a small, woody perennial herb that typically grows between 20–30 cm (8–12 inches) tall. It has tiny, oval-shaped leaves that are green-gray in color and a distinctive, pungent aroma. The plant produces small, purple or white flowers that bloom during the summer. Thyme thrives in well-drained, sunny soil and can be found growing wild in fields and rocky hillsides. It is also widely cultivated in herb gardens for both culinary and medicinal purposes.
Health Benefits of Raw Thyme:
Thyme contains essential oils, flavonoids, tannins, and phenolic compounds, all of which contribute to its impressive therapeutic benefits. Some of the key health benefits of raw thyme include:
Antimicrobial and Antibacterial Properties:
Thyme is known for its powerful antimicrobial properties, which help to fight off harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
It has been used traditionally to treat respiratory infections, digestive issues, and skin conditions due to its ability to inhibit the growth of pathogens.
Respiratory Health:
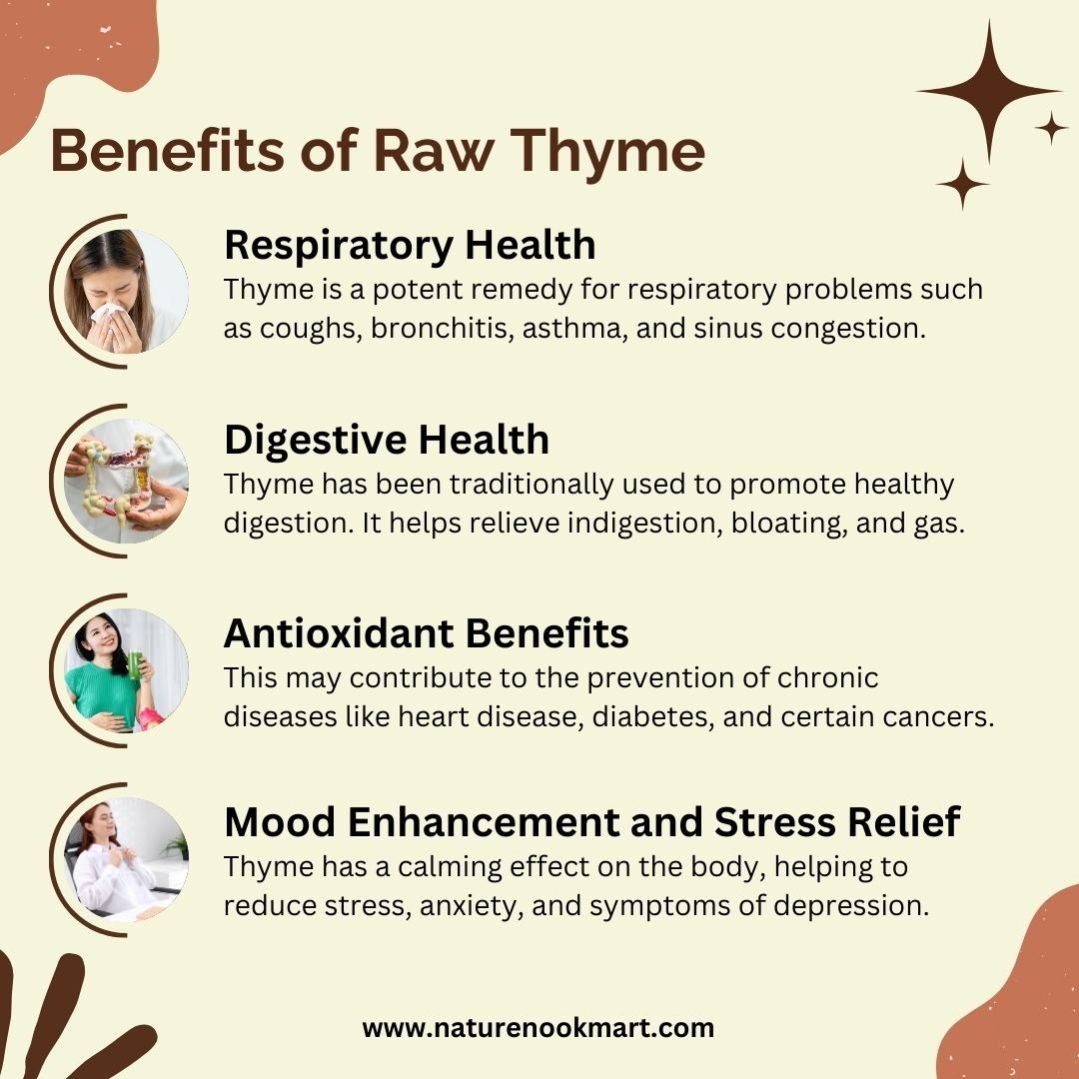
Thyme is a potent remedy for respiratory problems such as coughs, bronchitis, asthma, and sinus congestion.
The herb acts as an expectorant, helping to clear mucus from the lungs and relieve symptoms of respiratory discomfort.
Anti-inflammatory Effects:
The compounds in thyme, such as rosmarinic acid, have strong anti-inflammatory effects that can help reduce inflammation in the body.
This makes thyme useful for conditions like arthritis, muscle pain, and digestive inflammation.
Digestive Health:
Thyme has been traditionally used to promote healthy digestion. It helps relieve indigestion, bloating, and gas.
It can also stimulate appetite and improve overall gastrointestinal function.
Antioxidant Benefits:
Thyme is rich in antioxidants, which help protect the body from oxidative stress and the damage caused by free radicals.
This may contribute to the prevention of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Mood Enhancement and Stress Relief:
Thyme has a calming effect on the body, helping to reduce stress, anxiety, and symptoms of depression.
The herb is used in aromatherapy and herbal teas for its mood-boosting and calming properties.
Skin Health:
The antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties of thyme make it effective in treating acne, eczema, and other skin conditions.
It can be applied topically to disinfect wounds and soothe irritation or itching.
Culinary and Medicinal Uses of Raw Thyme:
Raw Leaves: Fresh thyme leaves can be used in a variety of savory dishes, such as soups, stews, meats, vegetables, and sauces. It pairs well with herbs like rosemary, garlic, and oregano.
Thyme Tea: Steeping fresh thyme leaves in hot water creates a soothing herbal tea, which can help with respiratory issues, digestion, and stress relief.
Essential Oil: Thyme essential oil is widely used in aromatherapy, massage, and as a topical treatment for various ailments. It is also an ingredient in many cleaning products due to its antibacterial properties.
Topical Use: Fresh thyme leaves can be crushed and applied to the skin to treat minor wounds, acne, or other irritations.
Cultural and Historical Significance:
Thyme has a long history of use in ancient cultures. In ancient Egypt, thyme was used in embalming and as a preservative. The Greeks and Romans used it to flavor foods and in medicine. Thyme was also believed to have protective properties and was used in the Middle Ages to ward off disease and evil spirits. It continues to be an important herb in culinary and herbal traditions around the world.
Nutritional Composition of Raw Thyme:
Vitamins: Rich in Vitamin C, Vitamin A, and small amounts of B-vitamins.
Minerals: Contains calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, and manganese.
Bioactive Compounds: Thymol, carvacrol, rosmarinic acid, flavonoids, and essential oils.
Calories: Low-calorie, with a high content of fiber and antioxidants.
Environmental Role and Cultivation:
Thyme is a hardy plant that thrives in well-drained, slightly alkaline soil and enjoys full sunlight. It is highly drought-tolerant once established and can grow in rocky, poor soil. Thyme is often cultivated in herb gardens and is a great companion plant, helping to repel certain pests in vegetable gardens. It is also a valuable plant for attracting pollinators like bees and butterflies.
|














.jpg)










Siddharth Rao
2025-02-18 15:39:23Nature Nook’s organic raw thyme is pure, fragrant, and perfect for cooking!