|
Moringa, often called the "Drumstick Tree" or "Miracle Tree," is a fast-growing, drought-resistant tree native to the Indian subcontinent. Renowned for its nutritional richness and medicinal properties, every part of the moringa tree, including its leaves, pods, seeds, and roots, is utilized in traditional medicine and as a superfood. Raw moringa, especially its fresh leaves, is a powerhouse of essential nutrients and health benefits.
Botanical Characteristics:
Moringa is a deciduous tree that grows up to 10–12 meters (33–39 feet) tall. It has feathery, bright green leaves, fragrant white flowers, and long, slender seed pods resembling drumsticks. The leaves are tender and oval-shaped, with a slightly earthy and peppery flavor when raw.
Health Benefits of Raw Moringa:
Raw moringa leaves are exceptionally nutrient-dense and packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants:
Nutritional Powerhouse:
Rich in Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and Vitamin E, supporting immune health and skin vitality.
Contains essential minerals like calcium, iron, potassium, and magnesium, vital for bone health and energy production.
Antioxidant Properties:
Fights oxidative stress with compounds like quercetin and chlorogenic acid.
Protects cells from free radical damage and promotes longevity.
Supports Energy and Vitality:
Improves energy levels naturally due to its high nutrient content.
Helps combat fatigue and supports overall well-being.
Promotes Healthy Digestion:
High in dietary fiber, aiding digestion and promoting gut health.
Natural detoxifying properties support liver function.
Anti-Inflammatory Benefits:
Reduces inflammation in the body, aiding conditions like arthritis and muscle soreness.
Regulates Blood Sugar and Cholesterol:
Helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels and supports heart health.
May reduce bad cholesterol (LDL) levels and improve circulation.
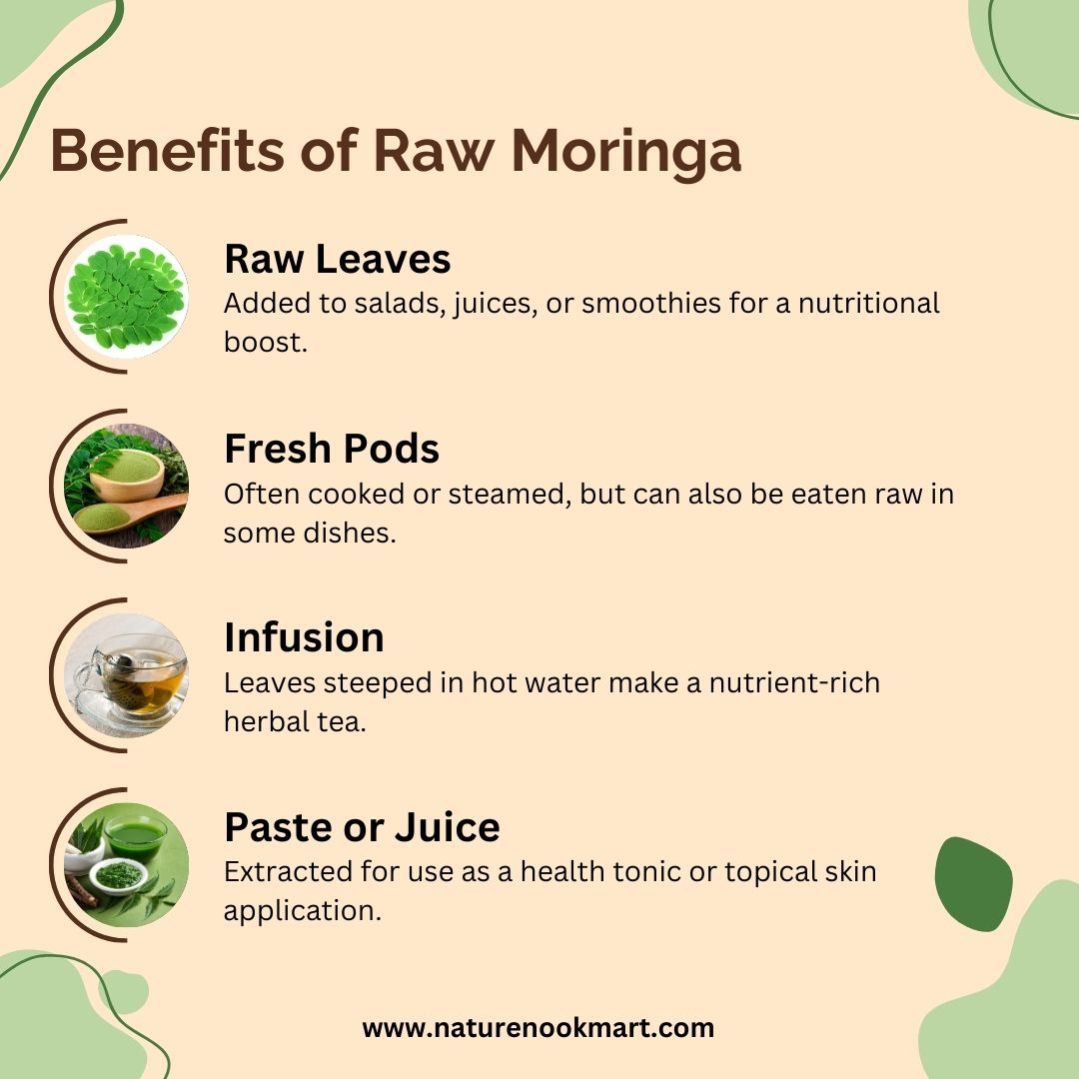
Culinary and Medicinal Uses of Raw Moringa:
Raw Leaves: Added to salads, juices, or smoothies for a nutritional boost.
Fresh Pods: Often cooked or steamed, but can also be eaten raw in some dishes.
Infusion: Leaves steeped in hot water make a nutrient-rich herbal tea.
Paste or Juice: Extracted for use as a health tonic or topical skin application.
Cultural and Historical Significance:
Moringa has been a cornerstone of traditional medicine in Ayurveda and other healing systems for thousands of years. Known as “Shigru” in Sanskrit, it is described as a natural remedy for over 300 ailments. Its significance has grown globally as a superfood for combating malnutrition and promoting health.
Nutritional Composition of Raw Moringa Leaves:
Vitamins: High in Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, and B-complex vitamins.
Minerals: Rich in iron, calcium, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus.
Proteins: Contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a plant-based protein source.
Calories: Low-calorie, with high fiber and nutrient density.
Environmental Role and Cultivation:
Moringa is a highly sustainable crop that grows in diverse climates and poor soil conditions. It is drought-resistant and requires minimal water, making it an eco-friendly choice for farming. The tree also contributes to soil enrichment and erosion prevention.
|











.jpg)




.jpg)


