|
Chamomile is a well-known herb used for its calming and soothing properties. It is one of the oldest and most widely used medicinal plants in the world. Raw chamomile, particularly in its fresh flower form, has a delicate, apple-like fragrance and offers a variety of therapeutic benefits, particularly for promoting relaxation, aiding digestion, and improving sleep.
Botanical Characteristics:
Chamomile is a small, herbaceous plant with feathery, green leaves and daisy-like flowers that are white with yellow centers. The flowers have a distinct, sweet aroma that is both soothing and calming. Chamomile typically grows to a height of 30–60 cm (1–2 feet) and is commonly found in fields, meadows, and gardens. It thrives in well-drained soil and requires moderate sunlight.
Health Benefits of Raw Chamomile:
Chamomile is rich in bioactive compounds like apigenin, bisabolol, and flavonoids, which contribute to its therapeutic effects. Some of the key health benefits include:
Relaxation and Stress Relief:
Chamomile is renowned for its calming properties, making it an effective natural remedy for reducing stress and anxiety.
It promotes relaxation by soothing the nervous system and helps with insomnia by improving sleep quality.
Digestive Health:
Chamomile aids digestion by relieving bloating, indigestion, and gas.
It is often used to treat stomach cramps, nausea, and upset stomachs, and helps to calm the digestive tract.
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties:
Chamomile contains powerful anti-inflammatory compounds that help reduce inflammation in the body, supporting conditions like arthritis and muscle pain.
Its antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals, promoting overall health and wellness.
Immune Support:
Chamomile is beneficial in boosting the immune system, helping to fight off infections like colds and flu.
It has mild antibacterial properties that can help prevent the spread of harmful bacteria in the body.
Skin Health:
Chamomile has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties that make it useful for treating skin irritations, cuts, and burns.
It helps to soothe conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and acne and promotes overall skin health.
Pain Relief:
Chamomile has mild analgesic properties and is often used to relieve headaches, menstrual cramps, and muscle aches.
It can also be used topically for pain relief in sore muscles or joints.
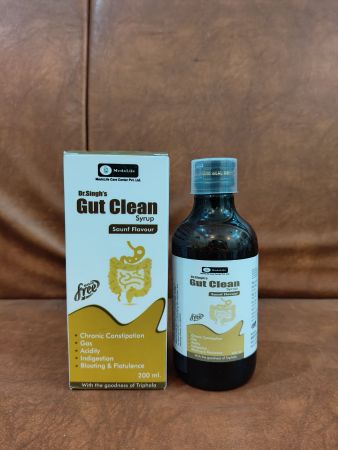
Culinary and Medicinal Uses of Raw Chamomile:
Raw Flowers: Fresh chamomile flowers can be used in salads, smoothies, or as a garnish for desserts.
Chamomile Tea: Chamomile flowers are often steeped in hot water to create a soothing herbal tea, which is widely known for its calming effects.
Topical Use: Crushed chamomile flowers or fresh extracts can be applied directly to the skin to treat minor wounds, rashes, or burns.
Chamomile Compress: A compress made from chamomile tea can be applied to inflamed or irritated skin.
Cultural and Historical Significance:
Chamomile has a long history of use in both Western and Eastern herbal traditions. In ancient Egypt, it was used to treat fevers and promote relaxation. The plant’s healing properties were also utilized in ancient Greek and Roman medicine. Today, chamomile remains a popular herb in traditional medicine, particularly for sleep disorders, anxiety, and digestive issues.
Nutritional Composition of Raw Chamomile:
Vitamins: Contains Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and small amounts of B-complex vitamins.
Minerals: Includes calcium, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus.
Bioactive Compounds: Apigenin, bisabolol, flavonoids, and essential oils.
Calories: Low-calorie and high in fiber.
Environmental Role and Cultivation:
Chamomile is a hardy, drought-tolerant plant that thrives in sunny areas with well-drained, sandy soil. It is often grown in herb gardens, meadows, or fields and is beneficial to the local ecosystem by attracting pollinators like bees and butterflies. Chamomile is easy to cultivate and can even be grown in containers for home use.
|





.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
1.jpg)
2.jpg)


.jpg)


.jpg)